What is glass?
Glass is a solid material without a uniform crystalline structure and possesses the property of transparency, allowing light to pass through relatively easily.
Glass is typically created by melting mineral compounds, often silicates such as sodium silicate and calcium silicate, and then rapidly cooling to form a hard and transparent material. What is unique about glass is its lack of a crystalline structure, meaning that the atoms or molecules in glass are not arranged in an ordered manner as in other crystals. Instead, they form an irregular structure, leading to the non-crystalline properties of glass.
History of glass
Ancient period
Natural glass is an essential part of Earth’s history and occurs spontaneously in nature following natural events and specific natural phenomena. It forms when various types of rocks melt due to high temperatures, and then they rapidly cool and solidify.
A famous example of natural glass is obsidian, a volcanic glass, which is formed following volcanic eruptions. Obsidian possesses hardness and sharpness, making it a valuable tool during the Stone Age, and it was used by ancient people to craft tools such as knives and drills.

However, the origins of artificial glassmaking and its development remain a significant question for the scientific community. We still do not know exactly when and where this process began. Although there are early traces of artificial glassmaking in human history, ongoing tracking and specific research are needed to gain a more detailed understanding of how artificial glassmaking emerged and evolved over time.
According to some sources, knowledge of artificial glassmaking may have appeared thousands of years ago in Mesopotamia (the present-day region of Iraq), where glass containers were possibly produced around 1500 BCE. Mesopotamia was one of the earliest civilizations with advanced technology and artistry, and they had the ability to melt sand and soda to create artificial glass.
Middle Ages
The 13th and 14th centuries were pivotal periods in the history of glassmaking in Venice, Italy, and the development of the glass industry here contributed to one of the world’s most renowned glass production centers. Below is a more detailed insight into the issues you mentioned:
The Development of Glassmaking Art in Venice, Italy: The city of Venice had a unique position with its system of water canals and humid environment, making it an ideal hub for glassmaking art. In the 13th century, Venetians developed unique glass production techniques and designs. They used a mixture of glass containing soda, silica, and calcium to create both translucent and opaque glass. The combination of creativity and technical knowledge helped Venice become a leading glass production center.
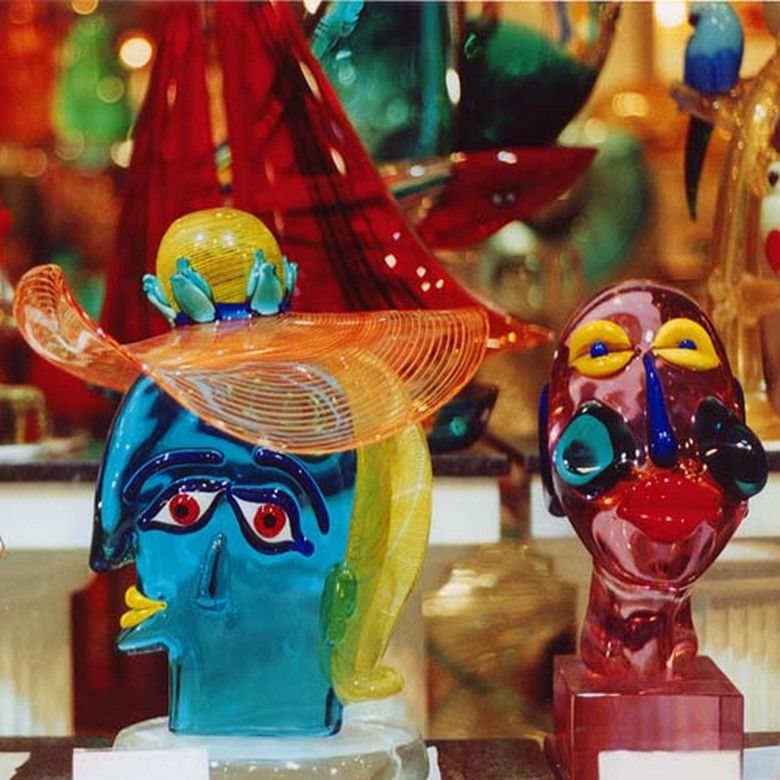

Murano Glass: Murano glass is a special type of glass produced on the island of Murano near Venice. Murano glass artisans are renowned for their talent and creativity. They have developed unique techniques such as millefiori (glass beads with diverse patterns) and latticino (thin glass threads inside glass beads). Murano glass has become an icon of the art of glassmaking in Venice.
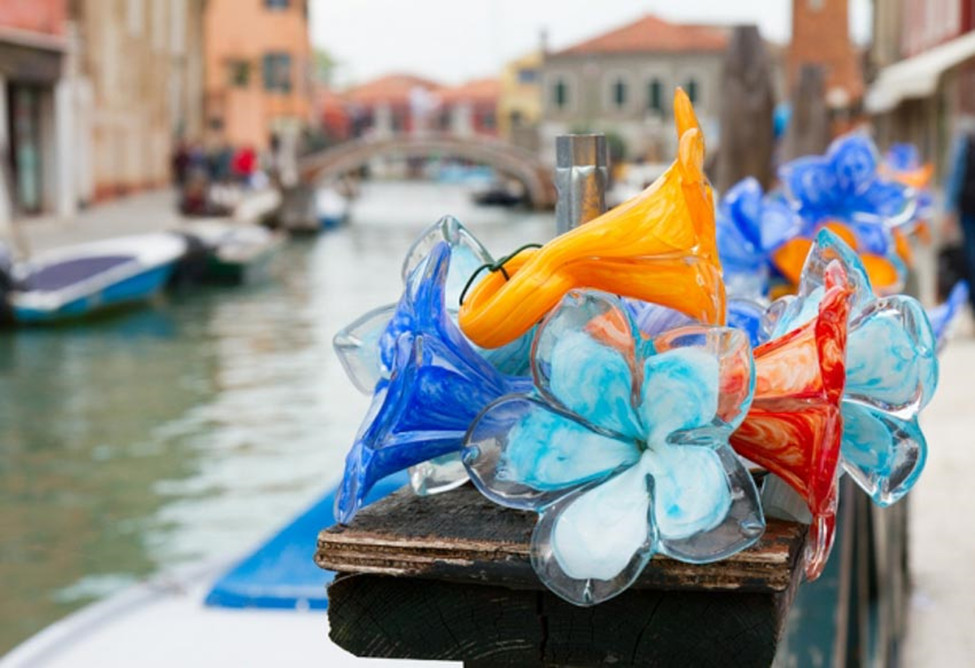

Glass as a Significant Commercial Commodity: Glass from Venice became a crucial commercial commodity in the 14th and 15th centuries. Venetian glass products, including mirrors, lamps, glass vases, and jewelry, were widely exported worldwide. Venice established trade relationships with numerous other countries, and Venetian glass became an integral part of global trade exchanges during that era.
In summary, the development of the glass industry in Venice, Italy, in the 13th and 14th centuries marked a significant period in the history of glassmaking. The combination of artistic creativity and technical knowledge resulted in unique glass products, making Venetian glass a vital commercial commodity in the international market.
Renaissance period
The Renaissance period is a crucial historical era in the development of art and glass in Europe. Here is a more detailed look at the role of glass during this period
Renaissance Period:
Advancement in Glass Art: The Renaissance, which spanned from the 14th to the 17th century, was a significant period of artistic and cultural development in Europe. During this era, the art of glassmaking made significant progress with the advancement of techniques and designs. Particularly, glass manufacturers in Venice (such as the Murano glassworks) continued to produce beautiful and unique glass products.
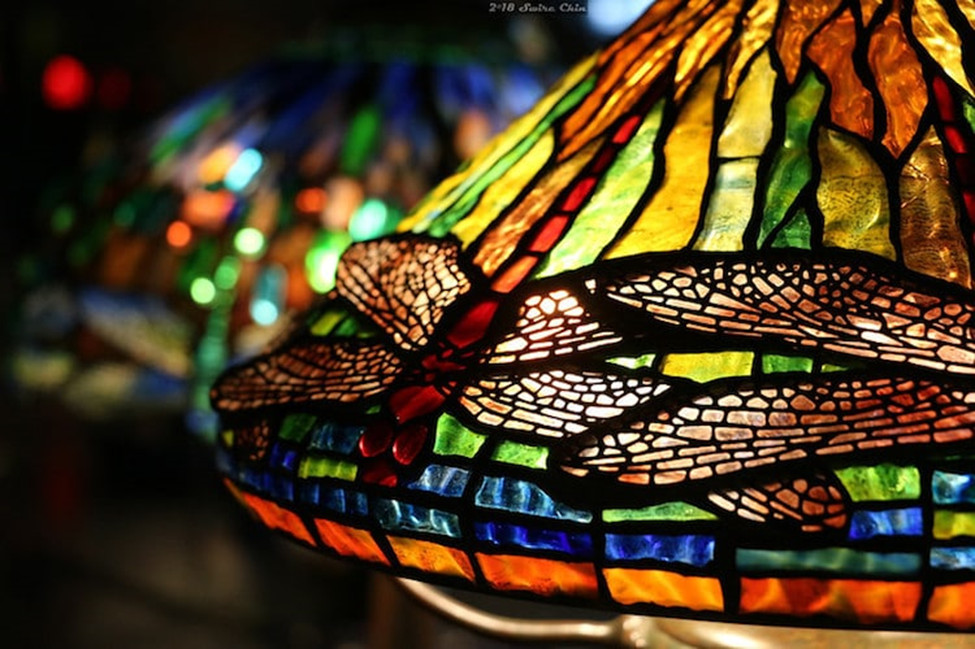

Applications in Art and Jewelry:
Glass became a significant part of art and jewelry during the Renaissance. Artists utilized glass to create unique and diverse artworks. In jewelry, glass was used to craft imitation gemstones with a wide range of colors, allowing for the alteration of the appearance of jewelry pieces.
Industrial Revolution period
Industrial Revolution: The Industrial Revolution, taking place from the 18th to the 19th century, had a profound impact on the glass industry and changed the way glass was produced and used in society. Here is a deeper look at the role of glass during this period:
Industrialization of Production: The Industrial Revolution marked a shift from manual craftsmanship to industrial production. The glass industry underwent this transformation as well. Glass manufacturers adopted machinery and advanced production processes to create large quantities of glass products at lower costs.
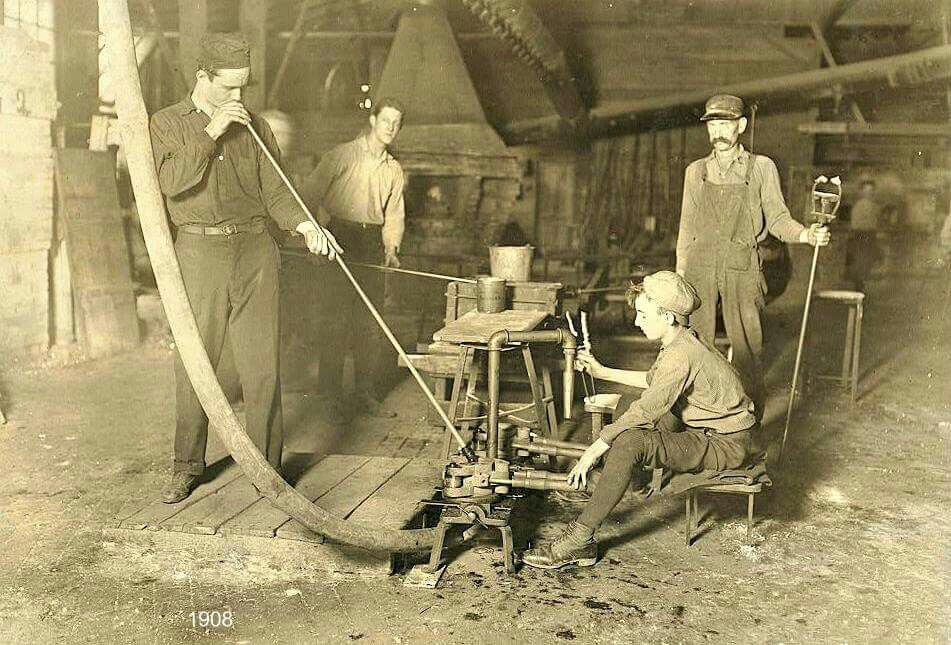

Enhanced Quality and Uniformity: The Industrial Revolution eliminated the costliness and irregularity associated with handmade glass production. New technologies allowed for better control of quality and consistency in glass products. This led to the creation of high-quality and more affordable glass products.
Development of Thermal Glass: During the Industrial Revolution, the advancement of thermal glassmaking technology (such as Pyrex glass) improved the heat resistance of glass. This had significant applications in the production of heat-resistant cookware, kitchen utensils, and medical equipment.
Diverse Applications: Glass became a crucial material in various fields during the Industrial Revolution. It was used in construction (windows and glass doors), medicine (chemicals and medical equipment), food (containers and food storage), and industry (glassware and bottles).
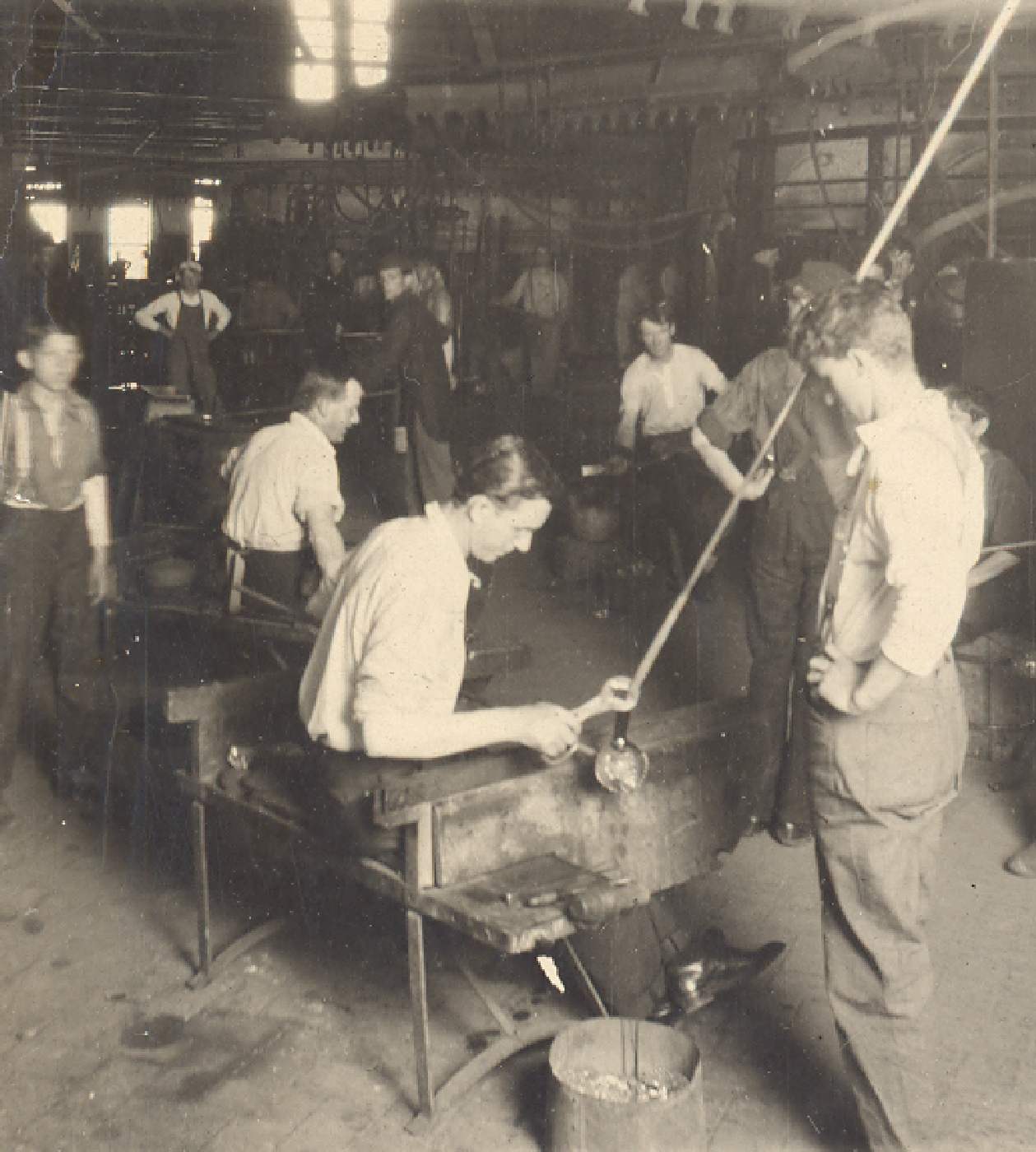
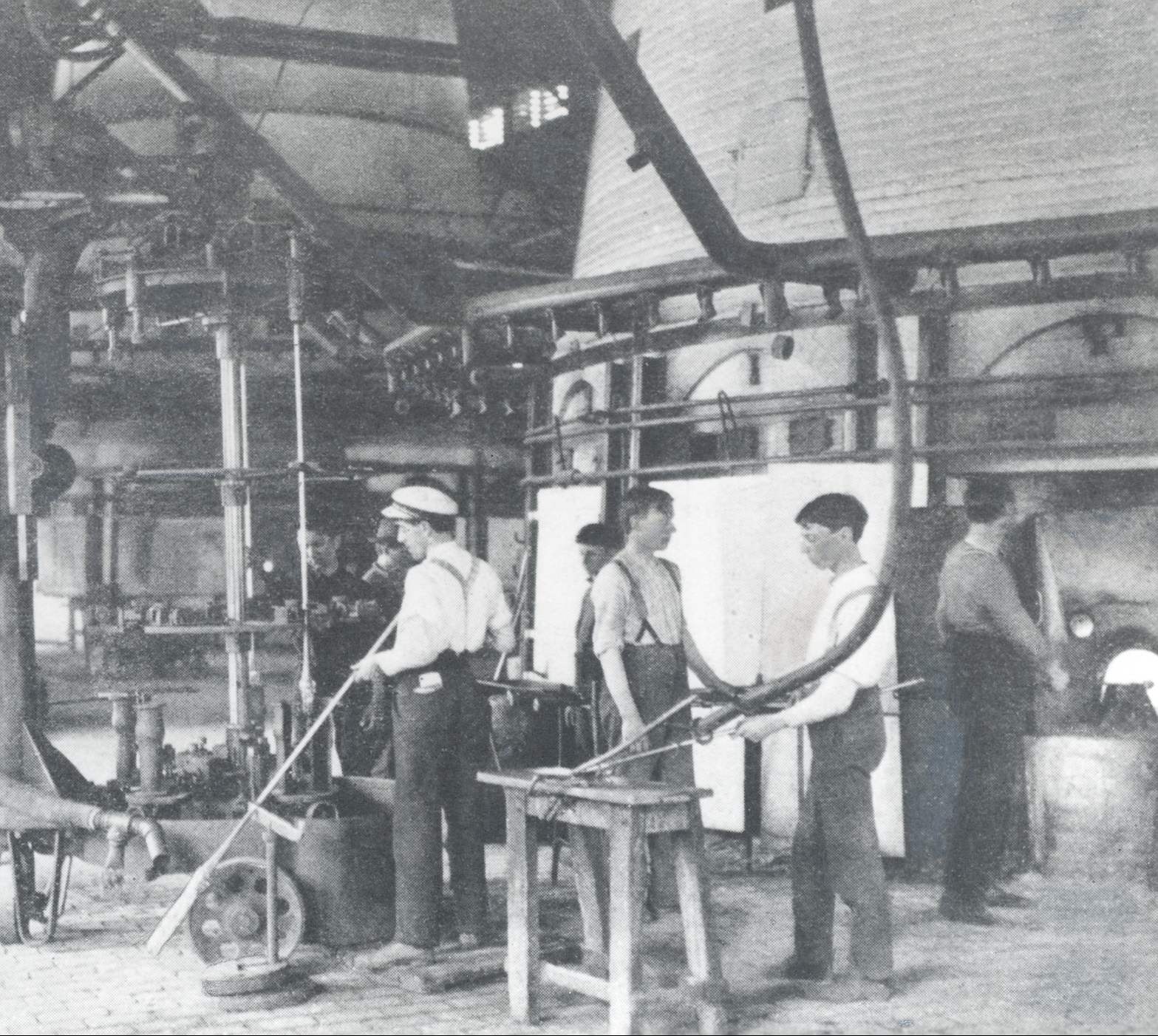

Glass Containers and Packaging Industry: The development of packaging and packaging industry during the Industrial Revolution led to the creation of glass jars and bottles for storing food, beverages, and other goods. This increased convenience and preservation of products, especially in the food and beverage industry.
In summary, the Industrial Revolution fostered the growth and widespread application of glass in various fields. The glass industry became an integral part of the industrial revolution, producing high-quality glass products and offering numerous opportunities for both industry and society.
Modern era
Glass in the Modern Era: Glass continues to play a crucial role in many aspects of daily life and industries in the modern era. Here are some key points about glass in the modern era:
Industry and Manufacturing: Modern glass has undergone significant developments in utilizing advanced technology for glass production. Automation and advanced manufacturing processes have helped create diverse and high-quality glass products with high production efficiency. Glass is used in various industries, from automotive and electronics to food packaging and healthcare.
Electronics and Information Technology: Glass has become an essential part of the electronics and information technology industry. It is used as screens and protection for mobile phones, tablets, LCD displays, and many other devices. Glass is also used in the production of electronic components such as test tubes and printed circuit boards.

Construction and Architecture: Glass in construction and architecture is becoming increasingly popular. Tempered and thermal glass helps create modern buildings with large windows and impressive glass structures. Glass is also used to craft unique architectural art pieces.
Medicine and Science: Glass continues to play a crucial role in the fields of medicine and science. It is used in the manufacturing of medical devices such as test tubes, vials, and analytical equipment. Glass also has widespread applications in scientific research, from storing laboratory samples to creating optical and analytical instruments.
Jewelry and Art: Glass remains a source of inspiration for jewelry and art. Glass artists create various unique and diverse works, from glass paintings shaping contemporary art to distinctive glass jewelry pieces.
In summary, in the modern era, glass not only plays a vital role in industry and daily life but also serves as a source of inspiration for art and creativity. Advanced technology has made glass a versatile and indispensable material in various fields.
Written by le duc duy
- ARCHITECT GLASS (2)
- DECOR GLASS (0)
- GLASS FOR BATHROOM (0)
- GLASS FOR KITCHEN (0)
- GLASS FOR LIVING ROOM (2)
- GLASS FURNITURE (0)
- BUILDING GLASS (0)
- GLASS CANOPY (0)
- GLASS DOOR (0)
- GLASS FLOOR (0)
- GLASS WALL – PARTITION (0)
- KNOWLEDGE (1)
- FLOAT GLASS (0)
- INSULATED G LASS (0)
- LAMINATED GLASS (0)
- TEMPERED GLASS (0)
STATISTICS
- 0
- 56
- 15
- 2,271
- 880,495
- 127,047
- 7
- 58

Leave a Reply